What Is a Pension Plan? How It Works and Why It Still Matters

Commitment to Our Readers
GOBankingRates' editorial team is committed to bringing you unbiased reviews and information. We use data-driven methodologies to evaluate financial products and services - our reviews and ratings are not influenced by advertisers. You can read more about our editorial guidelines and our products and services review methodology.

20 Years
Helping You Live Richer

Reviewed
by Experts

Trusted by
Millions of Readers
A pension plan is a retirement account funded and managed by your employer, guaranteeing income for life after you retire. Unlike a 401(k), a pension doesn’t rely on the stock market — your employer takes on the risk, not you.
While private-sector pensions are increasingly rare, they remain one of the most stable and valuable benefits for public employees, union members and long-tenured corporate workers.
Here’s how they work, who qualifies and how they fit into a modern retirement strategy.
Quick Stat:Only 15% of private-sector workers still have access to a traditional pension plan, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics — but 83% of state and local government employees do.
How a Pension Plan Works
At its core, a pension plan — also known as a defined-benefit plan — promises a guaranteed monthly payment in retirement. The amount depends on your salary, years of service and a formula your employer sets.

Employer-Funded Retirement Benefit
In a traditional pension, the employer funds and manages the account. You don’t have to choose investments or monitor market performance — your employer does that for you.
You “earn” your pension gradually through years of service. Once you reach your vesting period (typically 3-7 years), your benefit becomes permanent, even if you leave your job.
Defined Benefit vs. Defined Contribution Plans
Here’s how a pension plan compares to a 401(k):
| Feature | Pension Plan | 401(k) |
|---|---|---|
| Who funds it | Employer | Employee + employer match |
| Who manages investments | Employer | Employee |
| Guaranteed payout | Yes — lifetime income | Employer bears the risk |
| Risk level | Employer bears risk | Employee bears risk |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Tax treatment | Tax-deferred | Tax-deferred |
Takeaway: A pension plan guarantees stability and income for life. A 401(k) offers more flexibility and potential for higher returns, but with more risk.
How Pension Benefits Are Calculated
The formula is simple:
Years of Service x Final Average Salary x Employer Multiplier = Annual Pension BenefitExample: 30 years x $70,000 x 2% = $42,000 annual pension
Key Inputs:
- Years of Service: The longer you work, the larger your benefit.
- Salary: Usually based on your final or highest-average earnings.
- Multiplier: Set by your employer, often between 1.5% and 2%, per the U.S. Department of Labor.
Even a 0.5% change in your multiplier can mean thousands of dollars more in guaranteed annual income over a lifetime.
Pension Plan Example: How Much You Could Receive
| Worker | Years of Service | Final Salary | Multiplier | Annual Pension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public School Teacher | 30 | $70,000 | 2% | $42,000 |
| Corporate Employee | 25 | $80,000 | 1.5% | $30,000 |
Most defined-benefit plans replace 40% to 60% of pre-retirement income for long-term employees — enough to form a solid base for retirement.
Lump Sum vs. Monthly Pension Payments
When you retire, you can usually choose between a lump-sum payout or monthly lifetime payments.
| Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Lump Sum | Immediate access to funds; flexibility to invest | No guaranteed lifetime income; market risk |
| Monthly Payments | Predictable income for life; often includes survivor benefits | Less flexibility; limited inflation protection |
Rule of Thumb: Take monthly payments if you prefer long-term security and expect to live longer; take a lump sum if you have a strong investment plan.
Quick Stat:The average monthly benefit paid from private pension plans is about $1,775, according to the PBGC — though public-sector retirees often receive much more.
COLAs and Inflation Protection
Some pensions, especially government ones, include Cost-of-Living Adjustments (COLAs) to protect against inflation. Private pensions typically do not.
If your plan doesn’t include inflation protection, consider supplementing with a 401(k) or IRA for growth potential.
Types of Pension Plans
| Plan Type | Who Offers It | Federal, state and local employers |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Defined Benefit Plan | Public & private employers | Fixed payout for life based on salary and years worked |
| Cash Balance Plan | Some corporations | Hybrid of pension + 401(k) with interest credits |
| Government/Public Sector Pension | Federal, state and local employers | Includes COLAs and lifetime income |
| Union/Multi-Employer Plan | Labor unions | Covers multiple companies; negotiated benefits |
Tip: According to the BLS, government and union pensions generally offer stronger inflation protection than corporate plans, though the degree of protection can vary.
Pension Plan vs. 401(k) and Other Retirement Accounts
| Feature | Pension Plan | 401(k) | IRA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Who contributes | Employer | Employee + employer match | Employee |
| Guaranteed income | Yes | No | No |
| Investment control | Employer | Employee | Employee |
| Tax treatment | Deferred | Deferred | Depends on type |
| RMDs (Required Minimum Distributions) | Yes | Yes | Yes (Traditional IRA only) |
Fact Check: The PBGC reports that nearly 23,000 private pension plans are currently insured, covering over 31 million workers.
Why Pensions Offer Income Stability
A pension ensures a steady income for life — no worrying about stock market swings or outliving your savings. Private pensions are insured by the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC), which protects benefits up to $7,431 per month at age 65 in 2025.
Why 401(k)s Offer Flexibility and Growth Potential
A 401(k) gives you investment control and potential for higher returns. Many employers offer matching contributions, effectively adding “free money” to your savings.
However, 401(k) balances depend on market performance, and there’s no guaranteed income.
Quick Stat:The average 401(k) balance for workers in their 60s is about $232,000, according to Fidelity Investments (Q1 2025) — but lifetime pensions can easily pay that much or more over a 20-year retirement.
Who Still Gets Pension Plans in 2025
While most private companies have phased them out, several groups still enjoy pension benefits:
- Government Employees: The largest group with traditional defined-benefit pensions.
- Military and Public Safety Workers: Police officers, firefighters and military retirees.
- Union Members: Particularly in manufacturing, construction, and transportation.
- Legacy Corporate Plans: Older employees are still covered by pre-freeze agreements.
About one in six private-sector workers and four in five government workers are still enrolled in defined-benefit pension programs.
What Happens If Your Pension Plan Is Underfunded
The Role of the PBGC
If your employer can’t fund your pension, the PBGC steps in to ensure you still receive benefits — up to legal limits.
What To Do If Your Plan Is Underfunded:
- Review your annual funding statement.
- Check your PBGC coverage limits by age.
- Keep all plan documents for your records.
- If your plan freezes or ends, accrued benefits are still protected.
Learn more: Visit PBGC.gov for coverage details.
Quick Stat:The PBGC paid more than $7.4 billion in benefits to retirees in 2024 and insured over 24,000 private plans — protecting millions of Americans.
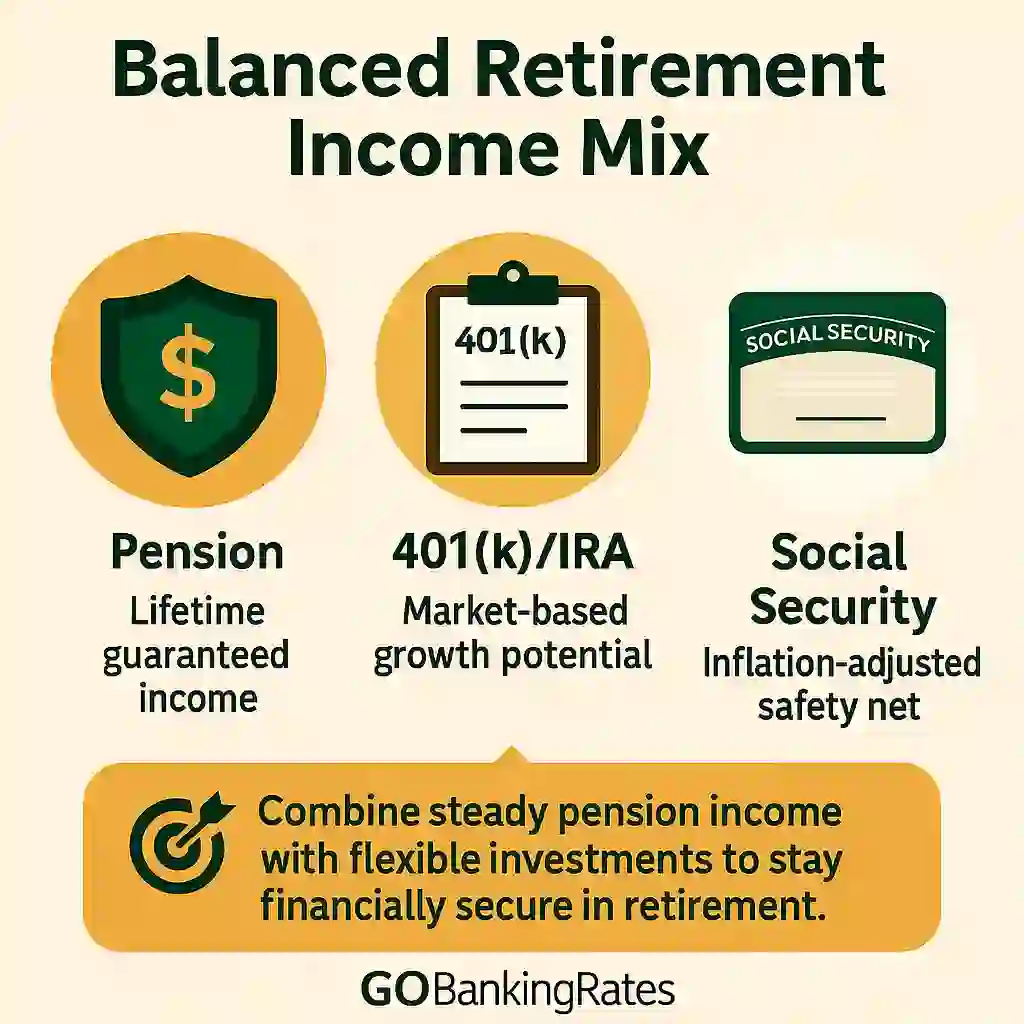
How Pensions Fit Into a Retirement Strategy
Think of your pension as the foundation of your retirement plan. You can then layer in other income sources like Social Security, a 401(k) or an IRA for added flexibility and growth.
Final Take to GO: Are Pension Plans Still Worth It?
Even though pension plans are rare today, they remain one of the few retirement options that provide true income security. If you’re one of the lucky few who still has one, it’s likely the cornerstone of your retirement income.
Understand your vesting schedule, payout options and benefit formula, then use your pension as a stable base to build the rest of your retirement plan around.
Next Step: Estimate how your pension fits into your overall strategy with the GoBankingRates Retirement Calculator.
FAQs
Here are the answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about pension plans and how they work:- What is the difference between a pension and a 401(k)?
- A pension plan gives you a guaranteed income for life; a 401(k) depends on your investments and contributions.
- Do pension plans still exist?
- Yes, but they are now most common in government, military/public safety and certain union sectors.
- Can I cash out my pension early?
- Usually not -- you must typically be vested and reach retirement age for full benefits.
- What happens to my pension if I leave the company?
- If you’re vested, you keep the earned benefit. Timing of access depends on plan rules. If not vested, you may lose it.
- Are pensions taxable?
- Yes -- pension income is generally subject to federal (and possibly state) tax when paid.
Information is accurate as of Oct. 20, 2025.
Our in-house research team and on-site financial experts work together to create content that’s accurate, impartial, and up to date. We fact-check every single statistic, quote and fact using trusted primary resources to make sure the information we provide is correct. You can learn more about GOBankingRates’ processes and standards in our editorial policy.
- USA.gov. "Retirement - usa.gov."
- Department of Labor. "Types of Retirement Plans | U.S. Department of Labor - dol.gov."
- Department of Labor. "Retirement Plans Benefits and Savings | U.S. Department of Labor - dol.gov."
- Benefits.gov. "Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation Pension Insurance - benefits.gov."
- IRS. "Topic No. 410 Pensions and Annuities - irs.gov."
- IRS. "Publication 575 (2019), Pension and Annuity Income - irs.gov."
- IRS. "A Guide to Common Qualified Plan Requirements - irs.gov."
- IRS. 2020. "Retirement Topics - Vesting | Internal Revenue Service - irs.gov."
 Written by
Written by  Edited by
Edited by 

























